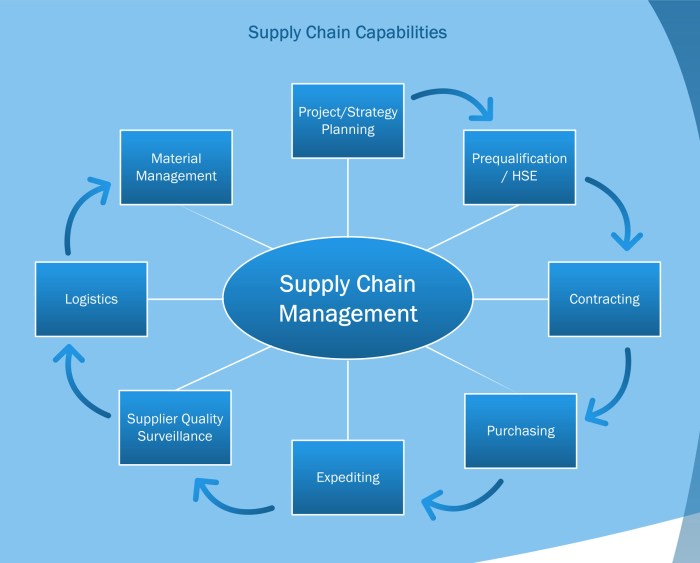
Supply chain management services are the backbone of modern commerce, encompassing the intricate network of processes involved in getting products from origin to consumer. From sourcing raw materials to final delivery, effective management ensures efficiency, profitability, and customer satisfaction. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of supply chain management, exploring its core components, benefits, challenges, technological advancements, and future trends.
We’ll examine various strategies, including lean and agile approaches, and discuss how businesses of all sizes can leverage technology and best practices to optimize their operations. Case studies of successful companies will highlight the tangible benefits of robust supply chain management, providing practical insights for readers seeking to improve their own operations.
Technological Advancements in Supply Chain Management
The modern supply chain is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by rapid technological advancements. These innovations are not merely incremental improvements; they represent a fundamental shift towards greater efficiency, transparency, and resilience. Data analytics, automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are reshaping how businesses manage their supply networks, leading to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
The Role of Data Analytics in Optimizing Supply Chain Operations
Data analytics provides unparalleled visibility into every aspect of the supply chain, from procurement to delivery. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources – including ERP systems, IoT sensors, and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms – businesses can identify bottlenecks, predict disruptions, and optimize resource allocation. For instance, predictive analytics can forecast demand fluctuations, allowing companies to adjust inventory levels accordingly and avoid stockouts or excess inventory.
Real-time data visualization dashboards provide managers with a clear overview of the entire supply chain, enabling proactive decision-making. This data-driven approach significantly reduces operational costs and improves overall efficiency.
Automation and Robotics in Transforming Supply Chain Processes
Automation and robotics are revolutionizing warehouse operations and logistics. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic arms are increasingly used for tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting, significantly improving speed and accuracy while reducing labor costs. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) optimize warehouse space utilization and streamline order fulfillment. Furthermore, automation extends beyond the warehouse; autonomous trucks and drones are being explored for last-mile delivery, promising faster and more cost-effective transportation.
The implementation of these technologies leads to increased throughput, reduced error rates, and enhanced overall productivity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Supply Chain Management
AI and ML algorithms are being deployed to address complex supply chain challenges. AI-powered demand forecasting models offer greater accuracy than traditional methods, leading to more effective inventory management. ML algorithms can detect anomalies and predict potential disruptions, allowing businesses to proactively mitigate risks. For example, an ML model can analyze historical data on weather patterns, transportation delays, and supplier performance to predict potential disruptions and suggest alternative solutions.
Furthermore, AI can optimize routing and scheduling, reducing transportation costs and delivery times. Companies like Amazon heavily utilize AI and ML for optimizing their vast and complex global supply chain.
Implementing a Warehouse Management System (WMS)
A flowchart illustrating the implementation of a Warehouse Management System (WMS):[Descriptive Text of Flowchart]The flowchart would begin with the “Initiation Phase,” encompassing needs assessment, vendor selection, and project planning. This leads to the “Implementation Phase,” detailing system configuration, data migration, and user training. The “Go-Live Phase” follows, involving system launch, initial testing, and user support. Finally, the “Optimization Phase” focuses on ongoing performance monitoring, system enhancements, and process improvements.
Each phase would have several sub-steps detailed within the flowchart’s boxes and connecting arrows to illustrate the sequential process. The overall flow would be linear, though iterative feedback loops would be depicted to highlight continuous improvement.
Supply Chain Management and Business Creation & Development

Effective supply chain management is fundamental to building a successful business. A well-structured and efficient supply chain can provide a competitive edge, enabling businesses to deliver products or services efficiently, cost-effectively, and reliably. This, in turn, fosters customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and ultimately, profitability and sustainable growth. The relationship between supply chain prowess and business success is deeply intertwined, influencing every stage from startup to expansion.Supply chain management significantly influences business creation by mitigating risks, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring timely delivery.
A robust supply chain strategy allows entrepreneurs to focus on core competencies like product development and marketing, rather than getting bogged down in logistical complexities. By establishing strong relationships with suppliers and distributors from the outset, new ventures can secure reliable sources of materials and distribution channels, fostering a strong foundation for growth. A well-defined supply chain also ensures that the right products are available at the right time and place, maximizing sales opportunities and minimizing waste.
Strategies for Building a Scalable and Resilient Supply Chain for a New Business
Building a scalable and resilient supply chain for a new business requires a strategic approach that considers both short-term needs and long-term growth. Key considerations include selecting reliable suppliers, implementing robust inventory management systems, and establishing flexible logistics networks. A scalable supply chain can adapt to increasing demand without significant disruptions, while resilience ensures that the business can withstand unexpected events, such as natural disasters or supply chain disruptions.
- Supplier Selection and Relationship Management: Thorough due diligence is crucial when choosing suppliers. Factors such as supplier reliability, financial stability, and ethical practices should be carefully evaluated. Building strong, collaborative relationships with key suppliers is essential for long-term success. This involves open communication, shared risk management, and mutually beneficial agreements.
- Inventory Management: Implementing an effective inventory management system is vital for balancing supply and demand. This includes using inventory tracking software to monitor stock levels, predicting future demand, and optimizing order quantities. Strategies like Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory can minimize storage costs and reduce waste, but require precise forecasting and reliable supplier relationships.
- Logistics and Distribution: Choosing appropriate logistics and distribution channels is crucial for timely and cost-effective delivery. Factors to consider include transportation modes (e.g., trucking, rail, air), warehousing strategies, and delivery networks. Leveraging technology, such as transportation management systems (TMS), can optimize routes, track shipments, and improve delivery efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: Building resilience into the supply chain requires anticipating and mitigating potential risks. This includes diversifying suppliers to avoid dependence on a single source, establishing contingency plans for disruptions, and investing in technologies that improve visibility and control across the supply chain.
The Role of Supply Chain Management in Business Growth and Expansion
Supply chain management plays a crucial role in facilitating business growth and expansion. As a business scales, its supply chain needs to adapt to increasing demand, new markets, and evolving customer expectations. Effective supply chain management enables businesses to expand their operations efficiently and cost-effectively, while maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction. This involves optimizing logistics, improving inventory management, and strengthening relationships with suppliers and distributors.
Furthermore, supply chain optimization can unlock opportunities for new product development, market entry into new regions, and improved profitability. For example, a company expanding internationally might need to establish new warehousing facilities, adapt its transportation network, and comply with local regulations. Efficient supply chain management helps navigate these complexities and ensure a smooth expansion.
Supply Chain Needs of Small Businesses Versus Large Corporations
While the fundamental principles of supply chain management apply to businesses of all sizes, there are significant differences in their needs and capabilities. Small businesses often have limited resources and rely on simpler, more agile supply chains. They may have fewer suppliers and rely heavily on personal relationships. Large corporations, on the other hand, often have complex, global supply chains involving numerous suppliers, intricate logistics networks, and sophisticated technologies.
They may utilize advanced analytics and forecasting tools to optimize their operations.
| Feature | Small Business | Large Corporation |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Relationships | Close, personal relationships with a limited number of suppliers | Formalized contracts with numerous suppliers, often globally dispersed |
| Technology | Basic inventory management systems, often manual processes | Advanced ERP systems, TMS, WMS, and other sophisticated technologies |
| Logistics | Simpler logistics networks, often relying on third-party logistics providers | Complex, global logistics networks, often involving multiple modes of transportation and warehousing facilities |
| Risk Management | Limited resources for risk mitigation, often relying on contingency planning | Dedicated risk management teams and robust contingency plans to mitigate potential disruptions |
Future Trends in Supply Chain Management
The landscape of supply chain management is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer expectations, and global events. Understanding and adapting to emerging trends is crucial for businesses to maintain competitiveness and resilience in the years to come. This section will explore key future trends, their potential impact, and strategies for proactive adaptation.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Growing consumer awareness of environmental and social issues is pushing businesses to prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing throughout their supply chains. This involves minimizing environmental impact through reduced carbon emissions, waste reduction, and responsible resource management. Ethical sourcing focuses on ensuring fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and responsible sourcing of materials, avoiding exploitation and human rights violations. Companies like Patagonia, known for their commitment to sustainable materials and ethical manufacturing, demonstrate the growing market demand for responsible practices.
Implementing robust supplier audits, traceability systems, and transparent reporting mechanisms are essential steps in achieving and demonstrating ethical and sustainable supply chain operations. Failure to adopt these practices can lead to reputational damage, decreased consumer loyalty, and increased regulatory scrutiny.
The Impact of Blockchain Technology on Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology offers a transformative potential for enhancing supply chain transparency and traceability. By creating a shared, immutable ledger of transactions, blockchain can track products from origin to consumer, providing real-time visibility into every stage of the supply chain. This increased transparency allows businesses to combat counterfeiting, improve product recall efficiency, and build greater trust with consumers. For example, Walmart utilizes blockchain to track its food supply chain, improving traceability and reducing foodborne illness risks.
The potential benefits extend to enhanced supply chain security, reduced fraud, and streamlined logistics processes. However, challenges remain in terms of scalability, standardization, and integration with existing systems.
Predictions for the Future of Supply Chain Management (Next 5-10 Years)
Over the next 5-10 years, we anticipate a continued convergence of technologies, driving greater automation, intelligence, and resilience in supply chains. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play a larger role in predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and inventory optimization. The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable real-time monitoring and control of assets and processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Furthermore, the focus on agility and resilience will intensify, as businesses seek to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions and geopolitical uncertainties. We can expect to see a greater emphasis on regionalization and diversification of sourcing to reduce reliance on single suppliers or geographical regions. Companies like Amazon, with its vast logistics network and sophisticated AI-driven systems, are already demonstrating the potential of these future trends.
Preparing for Future Trends and Challenges
Businesses can prepare for these future trends by investing in technology, developing robust data analytics capabilities, and fostering strong relationships with their supply chain partners. This includes adopting AI and ML tools for improved decision-making, implementing blockchain solutions to enhance transparency, and investing in training and development to upskill their workforce. Furthermore, building flexible and resilient supply chains through diversification and strategic partnerships is critical to navigating future uncertainties.
Proactive risk management, including scenario planning and contingency strategies, will be essential to mitigating potential disruptions. A proactive approach to sustainability and ethical sourcing, aligning with evolving consumer and regulatory expectations, will be vital for long-term success.
Mastering supply chain management is crucial for business success in today’s dynamic global landscape. By understanding the core principles, leveraging technological advancements, and adapting to emerging trends, organizations can build resilient, efficient, and profitable supply chains. This guide has provided a foundation for this understanding, equipping readers with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of this critical business function and drive sustainable growth.
Quick FAQs
What is the difference between supply chain management and logistics?
Logistics focuses on the efficient movement and storage of goods, while supply chain management encompasses the broader strategy of planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of goods, services, and information from origin to consumption.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my supply chain?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as on-time delivery, inventory turnover, order fulfillment cycle time, and customer satisfaction scores can help assess supply chain effectiveness.
What are some common supply chain risks?
Common risks include disruptions from natural disasters, geopolitical instability, supplier failures, cybersecurity threats, and unexpected demand fluctuations.
What role does sustainability play in modern supply chain management?
Sustainability is increasingly important, with businesses focusing on ethical sourcing, reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and promoting environmentally friendly practices throughout the supply chain.